Lateral Suture Vs TPLO surgeries are two options for treating cranial cruciate ligament (ccl) injuries in dogs. Both surgeries aim to stabilize the knee joint, but TPLO is generally considered more invasive and complex than lateral sutures. Lateral suture involves placing a strong suture material outside the knee joint to substitute the damaged ligament, whereas TPLO features a cut in the tibia bone that is then repositioned with a plate to change the joint’s angle and relieve stress on the cell.
Your veterinarian can advise you on the most appropriate course of action for your dog after the required diagnostics. A call rupture can be one of the hardest conditions a dog can experience. The cranial cruciate ligament is the leg’s common stabilizer and can be found in the knee joint in both canines and humans. Yet, several variables can influence whether a Ccl injury results in surgery. Obesity, genetics, age, and breeds all play a role in the likelihood of injury and the decision to undergo surgery. In general, the two primary options are lateral sutures and surgery for dogs experiencing Ccl tears.
Credit: kingsburgvet.com
Understanding Cruciate Ligament Injuries In Dogs
The knee joint is one of the largest joints in a dog’s body, composed of bones, cartilage, and ligaments. A torn cruciate ligament is a common injury that can occur due to trauma, genetics, or aging. The most common symptoms are limping, pain, and inflammation.
Treatment options consist of medical management or surgery, and tplo and lateral suture surgery are the most popular surgical choices. TPLO surgery involves cutting and rotating the bone to change the joint pressure, while lateral suture surgery involves adding an artificial ligament to the outside of the joint.
Surgical options should be discussed with a veterinarian, taking into consideration the dog’s size, activity level, and individual treatment needs.
Lateral Suture Approach
The lateral suture approach is a common technique used to correct cranial cruciate ligament rupture in dogs. This procedure involves the replacement of the damaged ligament with a surgical suture in the joint. During the surgery process, the surgeon will make an incision over the joint and remove the damaged tissues, then thread a suture through the bone and soft tissues to stabilize the joint.
While the lateral suture approach is a popular option due to its ease of use and simplicity, there are also some disadvantages like limited success rates and long recovery periods for some cases. The recovery time will vary depending on the dog’s age, overall health, and the success of the surgery.
TPLO Approach
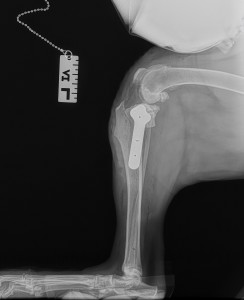
Tplo approach to or tibial plateau leveling osteotomy is a surgical procedure done to stabilize a dog’s knee joint after a ruptured cranial cruciate ligament. It involves cutting the upper part of the tibia bone, rotating it, and fixing it in place with a specially designed plate.
This procedure aims to change the dynamics of the joint and reduce the load on the healing ligament. The surgery requires anesthesia and post-operative care, which may take weeks to months. Its advantage over the traditional lateral suture approach is its higher success rate and faster recovery time.
However, it also comes with some drawbacks, such as higher costs, more complex procedures, and the need for experienced surgeons. If you are considering surgery for your dog, be sure to talk to your veterinarian about your options and the risks involved.
Comparing Lateral Suture And Tplo Approaches
Lateral suture and tplo are two common surgical approaches for canine cruciate ligament injuries. While both demonstrate success rates in clinical studies, some differences exist between the two in postoperative care requirements, effectiveness, cost, and expertise. Lateral suture tends to be less expensive and may require less skill in surgical implementation; however, it can require a longer recovery period with restricted activity.
Tplo typically allows for quicker recovery time but can be more costly and requires specialized expertise and equipment. Consideration should be given to the dog’s age, size, activity level, and overall health when weighing options. Successful outcomes are achievable with both techniques and examples available. Consultation with your veterinarian is suggested to determine the best approach for your pet.
FAQ Of Lateral Suture Vs TPLO Surgery On Dog
What Is Lateral Suture Surgery For Dogs?
Lateral suture surgery, or less, is a technique used to stabilize the knee joint of a dog with a partially torn or fully ruptured cranial cruciate ligament. It involves the placement of a strong suture in the stifle joint to replace the damaged ligament.
What Is Tplo Surgery For Dogs?
Tplo stands for tibial plateau leveling osteotomy. It is used to treat dogs with a completely ruptured cranial cruciate ligament. Tplo surgery involves cutting the bone, rotating it, and stabilizing it with plates, screws, or other implants.
Which Is A Better Surgery For My Dog, Lss, Or Tplo?
It depends on the severity of the injury, size, and age of the dog. Tplo surgery has been shown to have a higher success rate in larger or more active dogs, but it is also more invasive and expensive. Loss can be a good option for smaller or less active dogs.
How Long Is The Recovery Time For Both Surgeries?
The recovery time depends on the severity of the injury and the procedure performed. In general, expect at least 12 weeks for a full recovery. Less tends to have a shorter recovery period of eight to ten weeks, whereas tplo has a longer recovery of twelve to sixteen weeks.
Are There Any Risks Associated With Either Surgery?
As with any surgery, there are risks associated with both less and two. These include infection, bleeding, and anesthetic complications. However, these risks are minimized by choosing a qualified and experienced veterinarian and following proper post-operative care.
Conclusion
Choosing between the lateral suture and surgery for your dog is a decision that requires careful consideration. Both procedures have their advantages and disadvantages, and it’s vital to consult with your veterinarian to determine the best course of action for your pet’s specific case.
Tplo surgery provides a faster recovery time and can be beneficial for larger dogs, but it also comes with a higher price tag. On the other hand, lateral suture surgery is a more affordable option and recommended for dogs with less severe injuries.
Ultimately, the goal of any surgery is to restore your dog’s mobility and alleviate pain, and both lateral sutures and surgery have proven to be effective in achieving these objectives. Overall, this decision will ultimately be based on what’s best for your furry friend and their unique situation.