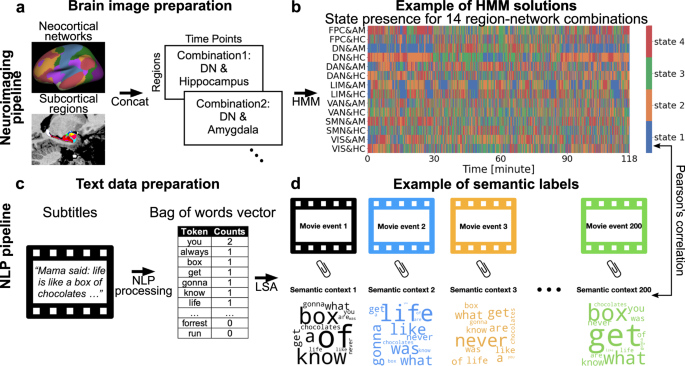
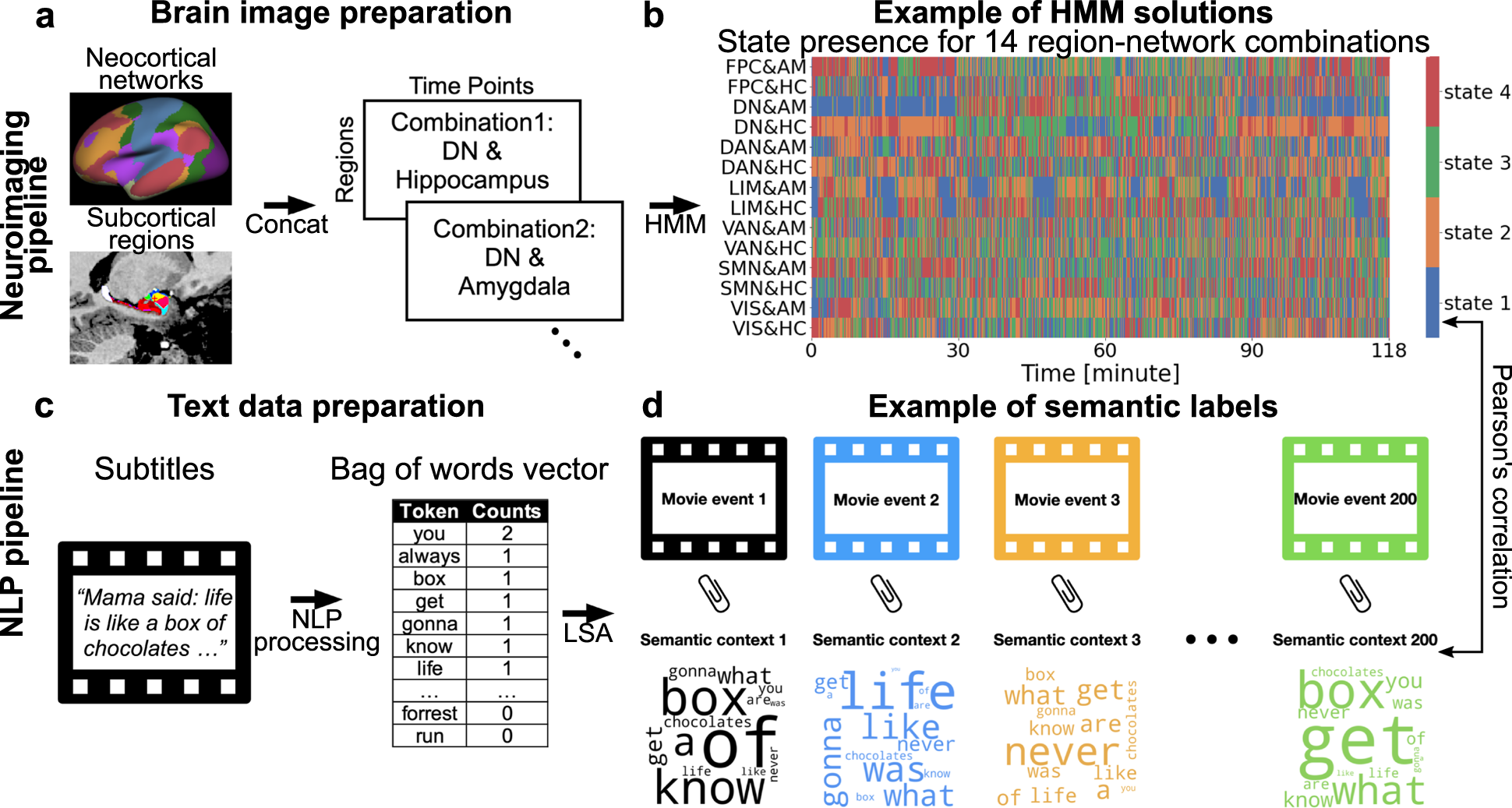
A dog may chase his tail in circles due to various reasons such as boredom, lack of physical activity, playfulness, anxiety, or underlying medical conditions. Tail chasing behavior is common in some breeds like Bull Terriers and German Shepherds.
It can also be a compulsive behavior similar to how humans engage in habits like nail-biting. The act of a dog chasing its tail in circles is often associated with overjoyed excitement, especially when they see someone they haven’t seen for a while.
However, if the behavior becomes excessive or obsessive, it is important to rule out any underlying health issues and seek the help of a behavioral specialist.
Credit: www.nature.com
Understanding Tail Chasing In Dogs
Tail chasing in dogs can indicate various things, including boredom, lack of physical activity, anxiety, or compulsive behavior. Understanding why your dog chases his tail in circles can help you address any underlying issues and provide the necessary care and training to prevent this behavior.
Does your dog engage in the intriguing behavior of chasing its tail in circles? While it may seem amusing or even adorable, tail chasing can actually be indicative of various underlying causes and conditions. To better comprehend this peculiar behavior, let’s explore the causes, behavioral patterns, and medical conditions associated with tail chasing in dogs.
Causes Of Tail Chasing
Tail chasing in dogs can stem from a multitude of reasons, including:
- Insufficient physical and mental stimulation
- Attention-seeking behavior
- Anxiety and stress
- Compulsive disorder
The breed of the dog can also play a role, with certain breeds being more prone to tail chasing behaviors such as Bull Terriers and German Shepherds.
Behavioral Patterns And Symptoms
When dogs engage in tail chasing, there are specific behavioral patterns and symptoms to look out for, such as:
- Intense focus and fixation on the tail
- Spinning in circles
- Biting or gnawing at the tail
- Excessive panting or salivating
- Agitation and restlessness
Additionally, tail chasing can disrupt a dog’s day-to-day activities, leading to decreased appetite, sleep disturbances, and difficulty concentrating on other tasks.
Medical Conditions Associated With Tail Chasing
While behavioral factors can contribute to tail chasing, it is crucial to rule out any underlying medical conditions that may be causing or exacerbating the behavior. Some medical conditions associated with tail chasing in dogs include:
| Condition | Symptoms |
|---|---|
| Fleas or parasites | Excessive itching and scratching, visible skin irritation |
| Anal gland issues | Scooting on their bottom, foul odor |
| Orthopedic problems | Pain or discomfort in the tail area |
| Neurological disorders | Abnormal movements or coordination, seizures |
If you notice your dog chasing its tail persistently or see any concerning symptoms, it is best to consult with a veterinarian to determine the underlying cause and appropriate treatment.
By understanding the causes, behavioral patterns, and medical conditions associated with tail chasing, you can help your beloved companion lead a healthier, happier life. Remember, a happy dog is not just a tail-chasing dog but one that receives proper care, attention, and medical intervention if necessary.

Credit: www.facebook.com
Addressing Tail Chasing Behavior
Many dog owners have witnessed their furry friends chase their own tails in circles, often wondering why they engage in this behavior. While tail chasing can be a normal and harmless behavior in some cases, it can also be a symptom of an underlying issue. In this section, we will explore different methods for addressing tail chasing behavior in dogs.
Preventing Tail Chasing
Prevention is always better than cure when it comes to tail chasing behavior in dogs. By providing them with plenty of physical and mental stimulation, you can help prevent boredom and anxiety – two common triggers for compulsive behavior.
To prevent tail chasing:
- Ensure that your dog gets regular exercise. Daily walks, play sessions, and interactive toys can help burn off excess energy and keep them mentally stimulated.
- Provide your dog with plenty of toys and activities to keep them entertained when you are not around. Puzzle toys, treat dispensers, and chew toys can help keep their minds occupied and prevent boredom.
- Establish a consistent routine for your dog, including regular feeding times, walks, and play sessions. Dogs thrive on routine and structure, which can help reduce anxiety and compulsive behaviors.
Training And Behavioral Specialists
If your dog’s tail chasing behavior persists despite your efforts to prevent it, it may be beneficial to seek help from training and behavioral specialists. These professionals have the expertise and experience to assess your dog’s behavior and provide targeted training and behavior modification techniques to address the issue.
When choosing a training or behavioral specialist:
- Look for professionals who specialize in dog behavior and have experience working with compulsive behaviors.
- Ask for recommendations from your veterinarian or other dog owners who have dealt with similar issues.
- Ensure that the specialist uses positive reinforcement-based training methods that focus on rewarding desired behaviors rather than punishing unwanted ones.
Utilizing Medication For Compulsive Behavior
In severe cases of tail chasing behavior, medication may be necessary to help manage the behavior. Medication can help reduce anxiety and compulsive behaviors, making it easier for your dog to break the habit of tail chasing.
When considering medication:
- Consult with your veterinarian to determine if medication is the right option for your dog. They will consider your dog’s overall health, behavior history, and the severity of the tail chasing behavior.
- Understand that medication should be used in conjunction with training and behavior modification techniques.
- Follow your veterinarian’s instructions carefully regarding dosage and administration of the medication.
Remember, each dog is unique, and there is no one-size-fits-all solution for addressing tail chasing behavior. It may take time and patience to find the right combination of techniques and strategies that work for your dog. Through prevention, training, and if necessary, medication, you can help your dog overcome tail chasing and live a happier, healthier life.
Breed-specific Tail Chasing
While tail chasing is a behavior seen in dogs across various breeds, it is important to note that certain breeds have a higher tendency for this behavior. Understanding the breed-specific factors behind tail chasing can provide valuable insights into why your dog exhibits this behavior. Let’s explore some common breeds with tail chasing tendencies, research findings on tail chasing in different breeds, and the early onset of tail chasing in specific breeds.
Common Breeds With Tail Chasing Tendencies
Some dog breeds are more prone to tail chasing than others. Here are a few examples:
- Bull Terriers
- German Shepherds
- Doberman Pinschers
- Shiba Inus
Research Findings On Tail Chasing In Different Breeds
Studies have shown that tail chasing behavior can vary among different dog breeds. Research findings suggest that certain breeds may be genetically predisposed to exhibit this behavior. For example, a study conducted in Japan found significant tail chasing tendencies in Bull Terriers and German Shepherds. Understanding these breed-specific tendencies can help dog owners and trainers address the behavior effectively.
Early Onset Of Tail Chasing In Certain Breeds
In some breeds, tail chasing behavior can start at a young age. Early onset of tail chasing is commonly observed in Bull Terriers and Doberman Pinschers. It is believed that a combination of genetics, environmental factors, and breed characteristics contribute to the development of this behavior in these specific breeds. If you notice your puppy engaging in tail chasing, it’s important to address it promptly to prevent it from becoming a long-standing habit.

Credit: www.rover.com
Frequently Asked Questions For Why Does My Dog Chase His Tail In Circles
What Does It Mean When A Dog Spins Its Tail In A Circle?
A dog spins its tail in a circle when it’s overjoyed to see someone special, especially if they haven’t seen them recently. It’s a happy reaction, often seen in videos of military reunions with their dogs.
Why Does My Dog Bite His Tail And Run In Circles?
Dogs may bite their tails and run in circles due to compulsive behavior caused by anxiety and stress. It can become a habit that worsens over time. Certain breeds, such as Bull Terriers and German Shepherds, are more prone to this behavior.
What Breed Of Dog Chases Its Tail?
Certain breeds like Bull Terriers, German Shepherds, Doberman Pinschers, and Shiba Inus are known to chase their tails.
What Does It Mean To Chase Tails?
Chasing tails refers to engaging in futile or unproductive activities, like a dog chasing its own tail. It signifies putting effort without making progress or going in circles. Dogs might chase their tails due to boredom, excitement, dealing with fleas, or expelling excess energy.
Conclusion
There are various reasons why dogs chase their tails in circles. It could be due to boredom, excitement, dealing with fleas, or even expelling energy, especially in puppies. However, tail chasing can also be a sign of compulsive behavior or underlying medical conditions.
It is important to monitor your dog’s behavior and consult with a veterinarian if the tail chasing becomes excessive or concerning. Remember, each dog is unique, and understanding the reasons behind their behavior will help in providing the appropriate care and attention they need.