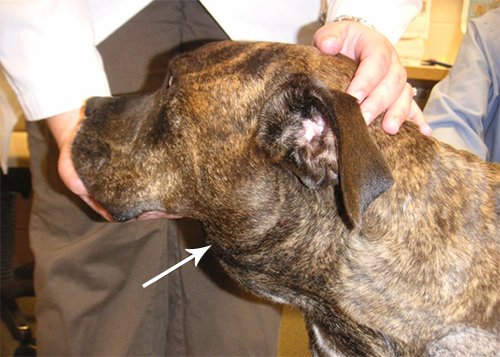
The first signs of lymphoma in dogs may include swollen lymph nodes and loss of appetite. Other symptoms can include vomiting, diarrhea, and weight loss, which may indicate a more advanced stage of the disease.
Lymphoma is a type of cancer that affects the lymphatic system, and early detection is crucial for successful treatment. Monitoring your dog for any abnormal signs or changes in behavior is important for identifying lymphoma in its early stages. Consulting a veterinarian for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan is essential for your dog’s well-being.
Understanding the signs of lymphoma and being proactive in seeking veterinary care can greatly improve the prognosis and quality of life for your furry companion.
Credit: ksvdl.org
Common Symptoms Of Lymphoma In Dogs
Lymphoma in dogs can present with various symptoms, including swollen lymph nodes, weight loss, decreased appetite, and lethargy. Pay attention to these early signs as they may indicate the presence of lymphoma in your furry friend.
Visible Physical Changes
Lymphoma, a type of cancer that affects the lymphatic system, can manifest in various ways in dogs. One of the first signs pet owners may notice is a visible physical change in their furry friend. These changes can include swollen lymph nodes, particularly in the neck, armpit, or groin areas. Your dog may also experience weight loss, which can be accompanied by decreased appetite. Skin changes, such as redness or lumps, may also be present. It is important to stay vigilant and consult a veterinarian if you notice any of these visible physical changes in your dog.Digestive Issues
When it comes to lymphoma in dogs, digestive issues can also be an early indicator of the disease. Your canine companion may exhibit symptoms such as vomiting, diarrhea, or a noticeable change in bowel movements. These digestive problems can be caused by the presence of lymphoma in the gastrointestinal tract, resulting in inflammation and disruption to normal digestion. If your dog experiences persistent digestive issues, it is crucial to seek veterinary attention to determine the underlying cause.Respiratory Problems
Dogs with lymphoma may develop respiratory problems as the disease progresses. If your furry friend is experiencing difficulty breathing, coughing, or wheezing, it could be a sign of lymphoma affecting the respiratory system. This can occur when the lymph nodes in the chest become enlarged, putting pressure on the airways and interfering with normal breathing patterns. If you notice any changes in your dog’s breathing or respiratory function, it is essential to consult a veterinarian promptly to ensure appropriate diagnosis and treatment.Lethargy And Weakness
Lymphoma can have a profound impact on a dog’s overall energy levels and strength. If your usually active and playful pet becomes lethargic, weak, or tires easily, it may be a warning sign of lymphoma. Cancer can deplete a dog’s energy reserves, leading to a noticeable decrease in their enthusiasm for regular activities. If you observe a significant change in your dog’s energy levels, it is important to consult a veterinarian who can evaluate their overall health and determine the underlying cause. Lymphoma is a serious condition that requires prompt veterinary attention. While these symptoms may indicate the presence of lymphoma, it is essential to remember that they can also be signs of other health issues. Early detection and diagnosis are key to providing the best possible care for your beloved canine companion. If you notice any of these common symptoms of lymphoma in your dog, reach out to your veterinarian for a thorough examination and guidance on the next steps.Early Warning Signs Of Canine Lymphoma
Early warning signs of canine lymphoma are crucial for pet owners to recognize, as early detection can significantly improve the prognosis and treatment outcomes for their beloved furry companions.
Enlarged Lymph Nodes
One of the earliest visible signs of lymphoma in dogs is the presence of enlarged or swollen lymph nodes. These can often be felt as firm, irregularly shaped lumps under the skin, particularly in the neck, under the jaw, in front of the shoulders, and behind the knees. Observing any unusual swelling in these areas should prompt an immediate veterinary evaluation.
Weight Loss
Unexplained weight loss is another telltale sign of lymphoma in dogs. If a pet owner notices that their dog is shedding pounds without any alterations to their diet or activity level, it could be indicative of an underlying health issue such as lymphoma. This loss of weight should be taken seriously and addressed promptly by a veterinarian.
Loss Of Appetite
A decreased or complete loss of appetite is often the result of lymphoma impacting a dog’s internal organs or gastrointestinal system. This can lead to a notable decline in a dog’s enthusiasm for food, which may prompt pet owners to seek medical attention. Paying attention to changes in eating habits is crucial in detecting lymphoma early.
Abnormal Behavior
Unusual changes in behavior can also serve as early indicators of lymphoma in dogs. These could include increased lethargy, decreased interest in playtime or walks, or even aggression or irritability that is out of character for the dog. Recognizing these behavioral changes allows pet owners to seek veterinary care promptly.
Specific Signs Of Lymphoma Based On Affected Areas
The specific signs of lymphoma in dogs can vary depending on which area of the body is affected. Understanding the signs based on the affected areas can help dog owners recognize the symptoms and seek veterinary care promptly. Below are the specific signs of lymphoma based on the affected areas.
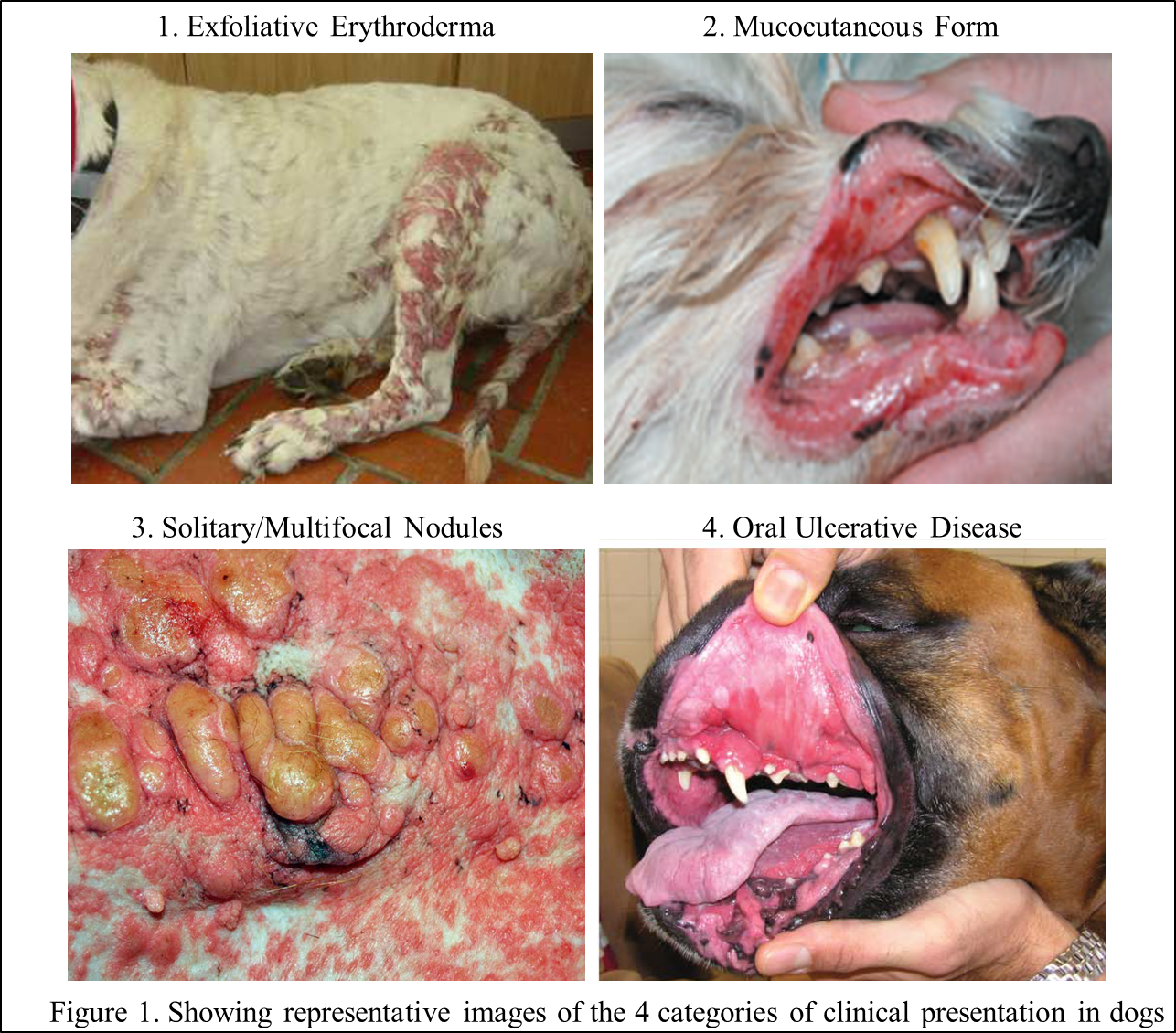
Cutaneous Lymphoma Symptoms
Dogs with cutaneous lymphoma may display symptoms such as:
- Red, ulcerated skin lesions
- Itchy or flaky skin
- Swelling of the lymph nodes near the skin
Gastrointestinal Lymphoma Symptoms
Gastrointestinal lymphoma in dogs can manifest in the following ways:
- Loss of appetite
- Vomiting and diarrhea
- Abdominal pain or bloating
Mediastinal Lymphoma Symptoms
If the mediastinal area is affected, dogs can show symptoms like:
- Coughing or difficulty breathing
- Enlarged lymph nodes in the chest
- Exercise intolerance
Multicentric Lymphoma Symptoms
Multicentric lymphoma, the most common form, may present with the following signs:
- Enlarged, non-painful lymph nodes throughout the body
- Lethargy and weakness
- Weight loss and decreased appetite

Credit: www.facebook.com
How To Recognize Lymphoma Symptoms In Dogs
Be Vigilant About Your Dog’s Health
Dogs are known for their ability to hide their pain and discomfort, so it’s important for you, as a responsible pet owner, to stay vigilant and observant about your dog’s health. Regularly monitoring your dog’s behavior, appetite, and overall well-being can help you catch any potential signs of lymphoma early on.
Regularly Inspect Lymph Nodes
One of the key signs of lymphoma in dogs is the enlargement of lymph nodes. Lymph nodes can be found in various locations throughout a dog’s body, including the neck, armpits, groin, and behind the knees. Regularly inspecting these areas and feeling for any lumps or bumps can help you detect potential early signs of lymphoma.
Notice Changes In Eating And Drinking
Dogs with lymphoma may experience changes in their eating and drinking habits. Keep a close eye on your dog’s appetite. Are they eating less than usual or showing disinterest in food? Additionally, monitor their water intake. Excessive thirst or increased frequency of drinking could be indicative of lymphoma.
Monitor Urination And Defecation Patterns
Changes in urination and defecation patterns can also be a sign of lymphoma in dogs. Pay attention to your dog’s bathroom habits. Are they urinating more frequently or having difficulty passing stool? Any abnormal changes in these patterns should be noted and discussed with your veterinarian.
Importance Of Early Detection And Diagnosis
The early detection and diagnosis of lymphoma in dogs are crucial for their well-being and overall prognosis. Identifying the initial signs and seeking veterinary care promptly can significantly impact the treatment options available, the prognosis of the disease, the quality of life of your furry friend, and the timely intervention and support they require.
Increased Treatment Options
The timely detection of lymphoma allows for a broader range of treatment options to be explored. When caught early, veterinarians can provide tailored treatment plans based on the specific type and stage of lymphoma. This may include chemotherapy, radiation therapy, immunotherapy, or a combination of treatments. With more options available, the chances of finding an effective treatment and achieving remission are heightened.
Improved Prognosis
Early detection and diagnosis bring a higher likelihood of a positive prognosis. By catching lymphoma in its early stages, the disease can be managed more effectively, potentially prolonging your dog’s life and improving their chances of survival. Swift intervention can prevent the disease from progressing and spreading to other organs, leading to a better overall outcome.
Enhanced Quality Of Life
When lymphoma is detected early, the treatments administered can aim not only to control the disease but also to maintain a good quality of life for your dog. These treatments can alleviate symptoms, reduce discomfort, and enhance their overall well-being. By proactively managing the disease, your furry companion can continue to enjoy their favorite activities and spend quality time with you.
Timely Intervention And Support
Early detection of lymphoma ensures that your dog receives the necessary intervention and support in a timely manner. Veterinarians can closely monitor the progression of the disease and make adjustments to the treatment plan as needed. Additionally, they can provide guidance and resources to help you navigate through the emotional and logistical challenges that come with caring for a dog with lymphoma.

Credit: www.imprimedicine.com
Frequently Asked Questions Of What Are The First Signs Of Lymphoma In Dogs
What Are The Common Signs Of Lymphoma In Dogs?
Common signs of lymphoma in dogs include swollen lymph nodes, weight loss, decreased appetite, lethargy, and abnormal growths. It is important to check for these signs regularly to catch lymphoma at its early stages for better treatment outcomes.
Can Lymphoma In Dogs Be Cured?
While lymphoma in dogs cannot be completely cured, it can be managed and treated. With early detection and proper treatment, dogs with lymphoma can experience extended periods of remission and a good quality of life.
What Tests Are Used To Diagnose Lymphoma In Dogs?
To diagnose lymphoma in dogs, veterinarians typically perform a physical examination, blood tests, X-rays, ultrasound, and a biopsy of the affected lymph node. These tests help confirm the presence of lymphoma and determine the stage of the disease.
Conclusion
To conclude, being aware of the first signs of lymphoma in dogs is crucial for early detection and treatment. From swollen lymph nodes to weight loss, loss of appetite, and lethargy, these symptoms should not be overlooked. Remember to consult with your veterinarian if you notice any unusual changes in your dog’s health.
By staying vigilant and proactive, you can increase the chances of successfully managing lymphoma in your furry friend.