You should stop fighting mast cell tumors in your dog when the risks and discomfort of treatment outweigh the potential benefits. Mast cell tumors in dogs can be tricky to manage, and decisions about treatment should be made in consultation with a veterinarian to ensure the best outcome for your pet.
Understanding the options available and being aware of the signs that the treatment is becoming too burdensome for the dog can help guide the decision-making process. It’s important to consider the dog’s quality of life and overall well-being when weighing the continuation of treatment.
This article discusses important factors to consider when deciding when to stop fighting mast cell tumors in dogs.
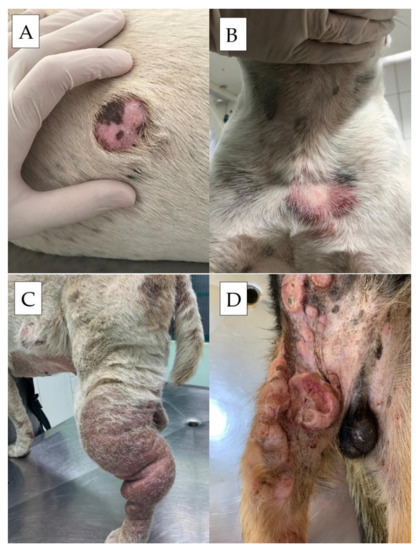
Credit: www.mdpi.com
Understanding Mast Cell Tumors In Dogs
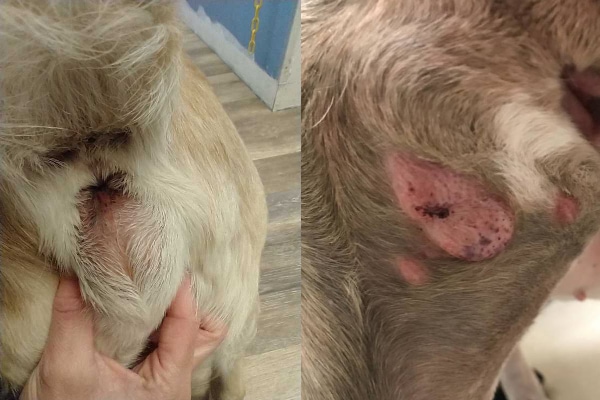
What Are Mast Cell Tumors? Mast cell tumors are a type of cancer in dogs that originate from a type of white blood cell. They can occur in the skin or other organs and can vary in size and aggressiveness.
Signs and Symptoms of Mast Cell Tumors Dogs with mast cell tumors may exhibit skin lumps, itching, vomiting, diarrhea, and loss of appetite. Additionally, the tumors can fluctuate in size and may cause discomfort.
Diagnosing Mast Cell Tumors in Canines Veterinary diagnosis of mast cell tumors involves a physical examination, blood tests, and imaging such as ultrasound or X-rays. A tissue biopsy is crucial for confirming the diagnosis.
Stages of Mast Cell Tumors and Prognosis Mast cell tumors are staged to determine the extent of the disease and guide treatment. The prognosis varies based on the tumor grade, location, and stage, and can range from good to guarded.
When To Stop Fighting Mast Cell Tumors In Dogs: Guides For Pet Owners
Knowing when to stop fighting mast cell tumors in dogs can be a challenging decision for pet owners. Assessing the quality of life of the dog is crucial in determining the appropriate course of action. Veterinary advice plays a significant role in guiding pet owners through this process, providing valuable insight into the treatment limitations and the dog’s response. Emotional and financial considerations for owners also play a vital role in making this difficult decision. It’s important for pet owners to carefully evaluate the overall well-being of their beloved dog and seek professional guidance to ensure the best possible outcome.
Evaluating Treatment Options
Traditional Treatment Methods: The traditional approach to treating mast cell tumors in dogs involves surgery, chemotherapy, and radiation therapy. Surgery aims to remove the tumor, while chemotherapy and radiation therapy may be used to target any remaining cancer cells.
Advances in Mast Cell Tumor Therapy: With recent advancements, targeted drug therapies such as tyrosine kinase inhibitors and immunotherapy have shown promising results in treating mast cell tumors in dogs. These treatments specifically target cancer cells, minimizing the impact on healthy cells.
Palliative Care Versus Curative Intent: When deciding on a treatment plan, it’s crucial to weigh the options between palliative care, which focuses on improving the dog’s quality of life, and curative intent, aimed at eradicating the cancer completely. Understanding the potential benefits and risks of each approach is essential for making informed treatment decisions for dogs with mast cell tumors.
Knowing When To Let Go
Deciding when to stop fighting mast cell tumors in your dog can be an incredibly difficult and emotional process. Understanding the signs of suffering, such as persistent pain, decreased quality of life, and loss of appetite, is crucial in making the difficult decision of whether euthanasia may be the kindest option. This can be a profoundly challenging choice, and it’s important to seek guidance from a veterinarian to determine the best course of action for your beloved pet. Coping with grief and loss following this decision is also an important aspect to consider for both your pet’s well-being and your own emotional health.
Supporting Your Dog Through The Journey
When to Stop Fighting Mast Cell Tumors in Dog
Comfort Measures for Affected Dogs
Mast cell tumors in dogs can be a challenging diagnosis to navigate. Implementing comfort measures is crucial to ensure your pet’s well-being. Providing a cozy and warm environment, gentle massages, and regular grooming to alleviate discomfort can help your furry friend feel more at ease. Additionally, addressing nutritional support and pain management is essential for managing the effects of mast cell tumors. Ensuring your dog receives a balanced diet and managing pain through medication prescribed by a veterinarian are crucial for their comfort. Moreover, offering emotional support and spending quality time with your dog can have a profound impact on their well-being during this difficult time.
Frequently Asked Questions For When To Stop Fighting Mast Cell Tumors In Dog
When Should I Consider Stopping Treatment For Mast Cell Tumors In My Dog?
It’s important to consider stopping treatment if your dog’s quality of life is significantly impacted, if treatment becomes too invasive, or if there’s evidence of significant disease progression despite therapy. Discuss with your vet to weigh the potential benefits and risks of continuing treatment.
What Are The Signs That The Treatment For Mast Cell Tumors May Not Be Effective?
Signs such as persistent growth of the tumor, continued ulceration, or symptoms of metastasis are indications that the treatment may not be effectively controlling the tumors. Regular monitoring and discussions with your vet can help assess the effectiveness of the current treatment plan.
How Can I Evaluate The Quality Of Life For My Dog With Mast Cell Tumors?
Assess your dog’s quality of life by monitoring their energy levels, appetite, pain, and enjoyment of everyday activities. If the side effects of treatment are impacting their well-being and joy, it may be time to consider stopping treatment. Regular communication with your vet is essential in making this decision.
Conclusion
Deciding when to stop fighting mast cell tumors in dogs is a complex and emotional decision. It’s important to consider the dog’s quality of life, the impact of treatment on them, and the guidance of a veterinarian. Ultimately, each case is unique, and weighing the benefits and drawbacks is essential in making the right decision for your furry friend.